What is Respiratory Disease
How it Affects Health | How to Treat | How to Use | Why Pulmogine
Basic Information
Credit: Stocky01. Freepik
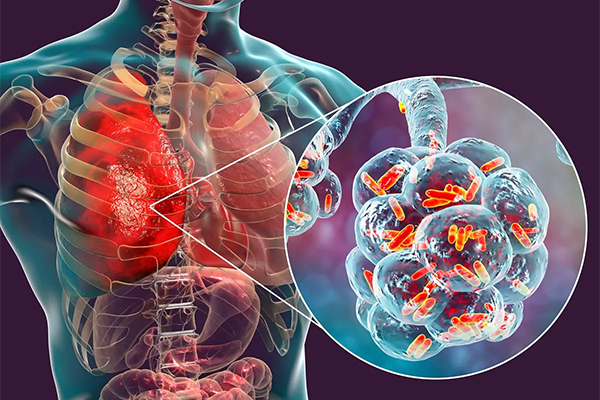
Respiratory diseases include various conditions that affect the lungs and airways influencing the process of breathing. These diseases are generally classified into two main categories: obstructive and restrictive.1 Below is an overview of some common respiratory conditions.1,2
Obstructive Respiratory Diseases
These diseases are characterized by a blockage or narrowing of the airways, which makes it difficult to exhale air fully.
- Asthma: Inflamed and narrowed airways, causing wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
- Emphysema: Destruction of lung air sacs (alveoli) causing breathing difficulty.
- Chronic Bronchitis: Inflammation of bronchial tubes, resulting in a chronic cough and mucus.
- Cystic Fibrosis: A genetic disorder leading to thick, sticky mucus that clogs airways and causes respiratory infections.
- Bronchiectasis: Permanent damage and widening of airways, causing chronic coughing and excessive mucus production.
Restrictive Respiratory Diseases
These diseases involve a reduction in lung volume, making it difficult to fully expand the lungs.
- Pulmonary Fibrosis: Scarring and stiffening of lung tissue, leading to difficulty with deep breathing.
- Interstitial Lung Disease: A group of disorders causing inflammation and scarring of lung tissue, impairing lung function.
- Pleural Effusion: Fluid buildup between the pleural layers, restricting lung expansion.
Infectious Respiratory Diseases
These include diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens.
- Pneumonia: Lung infection causing inflammation and fluid or pus in the alveoli.
- Tuberculosis (TB): Bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs, but can impact other body parts.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which can be acute (often viral) or chronic.
Other Notable Respiratory Conditions
- Sleep Apnea: Disorder with repeated breathing stops during sleep, often due to upper airway obstruction.
- Lung Cancer: Malignant lung tumors causing coughing, chest pain, and other respiratory symptoms.
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency: Genetic condition leading to lung and liver disease from a lack of a protective protein.
Prevalence
Respiratory diseases represent a significant global health challenge. The statistics are alarming:
Chronic respiratory diseases are a major global health issue, affecting 384 million people with COPD, which causes 3 million deaths annually. Tuberculosis impacts 10 million people each year, resulting in 1.6 million deaths, making it the most common lethal infectious disease. Lung cancer, the deadliest form of cancer, claims more than 7.6 million lives annually, while asthma affects 334 million people, including 14 percent of children—a number that is rising. Pneumonia also remains a significant cause of death, particularly among the young and elderly. Additionally, 91 percent of the global population lives in areas where air quality exceeds World Health Organization guidelines, worsening respiratory health risks.3

Credit: firsnet.org
Reference :
- Leader, D. (2023). Obstructive vs. Restrictive Lung Diseases: Causes and Treatment. Verywell Health.
- Martinez-Pitre, P. J., Sabbula B. R., Cascella M. (2023). Restrictive Lung Disease. National Center for Biotechnology Information. National Library of Medicine.
- Global Initiative for Asthma (2019). World Lung Day 2019: Respiratory groups unite to call for healthy lungs for all.