How it Affects Health
What is Nerve Pain | How to Treat | How to Use StimOn | Why StimOn
Causes
Nerve pain is usually caused by an injury or disease that affects the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) or the nerves that run to your muscles and organs. Common causes of nerve pain include: 1
- Injuries or trauma to the brain, spine, or nerves
- Poor blood supply to the nerves
- Alcoholism
- Vitamin B1 or B12 deficiency
- Phantom pain after an amputation
- Diabetes or stroke
- Hormonal imbalances
- Infections, such as shingles and HIV/AIDS
- Diseases, such as cancer, kidney disease, and autoimmune disorders
- Bone marrow disorders
- Fibromyalgia: Chronic pain, often linked to emotional distress or poor sleep
- Sciatica: Nerve pressure in the lower back that leads to leg pain, tingling, or weakness

Credit: Jodie Anne Phillips Polich, P.C
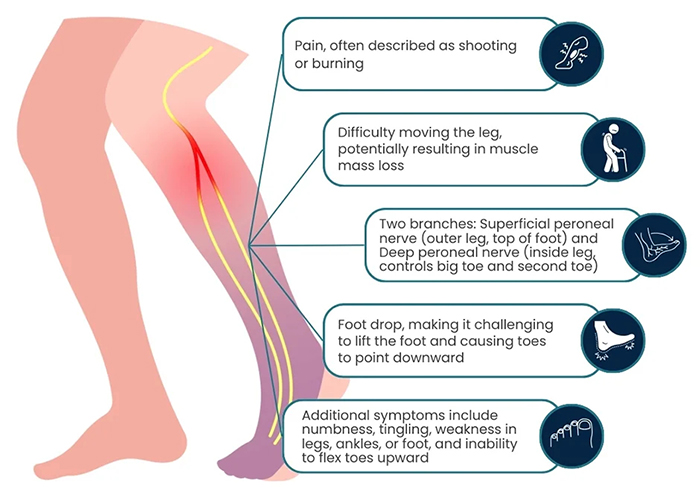
Symptoms
Patients typically describe the pain as a shooting, stabbing, or burning sensation. Common symptoms of nerve pain include: 1
- Sharp or shooting pain: Feels like electric shocks.
- Burning sensation: Persistent burning in the affected area.
- Tingling: A prickling sensation, often described as "pins and needles."
- Numbness: Lack of sensation in the affected area.
- Increased sensitivity: Pain triggered by normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia).
- Weakness: Muscle weakness associated with the affected nerve.

Credit: Dr. Boleslav Kosharskyy
Prevention
Preventing nerve pain involves a combination of lifestyle changes and health management strategies.1,2
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support nerve health.
Exercise Regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to improve circulation and maintain a healthy weight. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and yoga can be beneficial.
Manage Chronic Conditions: Control conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and autoimmune diseases through medication, diet, and regular check-ups.
Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco: Limit or eliminate alcohol consumption and avoid smoking, as both can damage nerves over time.
Protect Your Nerves: Use protective gear during activities that could lead to injury. For example, wear gloves when working with tools or participating in sports.
Maintain Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture, especially when sitting for long periods. Ergonomic workspaces can help reduce nerve compression.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your body and nerves functioning optimally.
Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga, as stress can exacerbate pain symptoms.
Regular Check-ups: Schedule routine check-ups to catch any underlying health issues early.
Educate Yourself: Learn about the risk factors for nerve pain and stay informed about ways to protect your nerve health.
Credit: Karelnoppe
Reference :
- Healthdirect. (n.d.). Nerve pain (neuralgia).
- Alabama Neurological Surgery & Spine. (2023). Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Nervous System.